|
|
Other result values or default value
|
|
|
DATE |
TIME
WITHOUT TIME ZONE |
TIMESTAMP
WITHOUT TIME ZONE |
TIMESTAMP
WITH TIME ZONE |
| Result value (any) |
DATE |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
TIME
WITHOUT TIME ZONE |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
TIMESTAMP
WITHOUT TIME ZONE |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
TIMESTAMP
WITH TIME ZONE |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y: Can be converted
N: Cannot be converted
- The data type of the return value will be the data type within the result or default value that is longest and has the highest precision.
**Example**
----
In the following example, the value of col3 in table t1 is compared and converted to a different value. If the col3 value matches search value 1, the result value returned is "one". If the col3 value does not match any of search values 1, 2, or 3, the default value "other number" is returned.
~~~
SELECT col1,
DECODE(col3, 1, 'one',
2, 'two',
3, 'three',
'other number') "num-word"
FROM t1;
col1 | num-word
------+----------
1001 | one
1002 | two
1003 | three
(3 rows)
~~~
----
#### 5.5.2 LNNVL
**Description**
Determines if a value is TRUE or FALSE for the specified condition.
**Syntax**
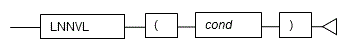
**General rules**
- LNNVL determines if a value is TRUE or FALSE for the specified condition. If the result of the condition is FALSE or NULL, TRUE is returned. If the result of the condition is TRUE, FALSE is returned.
- The expression for returning TRUE or FALSE is specified in the condition.
- The data type of the return value is BOOLEAN.
**Example**
----
In the following example, col1 and col3 of table t1 are returned when col3 has a value of 2000 or less, or null values.
~~~
SELECT col1,col3 FROM t1 WHERE LNNVL( col3 > 2000 );
col1 | col3
------+------
1001 | 1000
1002 | 2000
2002 |
(3 row)
~~~
----
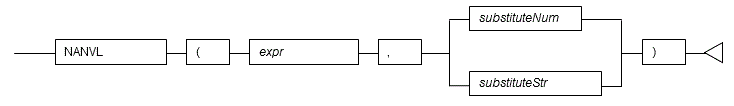
#### 5.5.3 NANVL
**Description**
Returns a substitute value when a value is not a number (NaN).
**Syntax**
**General rules**
- NANVL returns a substitute value when the specified value is not a number (NaN). The substitute value can be either a number or a string that can be converted to a number.
- For *expr* and *substituteNum*, specify a numeric data type. If *expr* and *substituteNum* have different data types, they will be converted to the data type with greater length or precision, and that is the data type that will be returned.
- For *substituteNum*, you can also specify a string indicating the numeric value.
- The data type used for the return value if a string is specified for the substitute value will be the same as the data type of *expr*.
**Example**
----
In the following example, "0" is returned if the value of col1 in table t1 is a NaN value.
~~~
SELECT col1, NANVL(col3,0) FROM t1;
col1 | nanvl
------+-------
2001 | 0
(1 row)
~~~
----
#### 5.5.4 NVL
**Description**
Returns a substitute value when a value is NULL.
**Syntax**

**General rules**
- NVL returns a substitute value when the specified value is NULL. When *expr1* is NULL, *expr2* is returned. When *expr1* is not NULL, *expr1* is returned.
- Specify the same data types for *expr1* and *expr2*. However, if a constant is specified in *expr2*, and the data type can also be converted by *expr1*, different data types can be specified. When this happens, the conversion by *expr2* is done to suit the data type in *expr1*, so the value of *expr2* returned when *expr1* is a NULL value will be the value converted in the data type of *expr1*. This is not necessary for types (numeric, int) and (bigint, int).
**Example**
----
In the following example, "IS NULL" is returned if the value of col1 in table t1 is a NULL value.
~~~
SELECT col2, NVL(col1,'IS NULL') "nvl" FROM t1;
col2 | nvl
------+---------
aaa | IS NULL
(1 row)
~~~
----
#### 5.5.5 NVL2
**Description**
Returns a substitute value based on whether a value is NULL or not NULL.
**Syntax**

**General rules**
- NVL2 returns a substitute value based on whether the specified value is NULL or not NULL. When *expr* is NULL, *substitute2* is returned. When it is not NULL, *substitute1* is returned.
- Specify the same data types for *expr*, *substitute1*, and *substitute2*. However, if a literal is specified in *substitute1* or *substitute2*, and the data type can also be converted by *expr*, different data types can be specified. When this happens, *substitute1* or *substitute2* is converted to suit the data type in *expr*, so the value of *substitute2* returned when *expr* is a NULL value will be the value converted to the data type of *expr*.
**Example**
----
In the following example, if a value in column col1 in table t1 is NULL, "IS NULL" is returned, and if not NULL, "IS NOT NULL" is returned.
~~~
SELECT col2, NVL2(col1,'IS NOT NULL','IS NULL') FROM t1;
col2 | nvl2
------+---------
aaa | IS NULL
bbb | IS NOT NULL
(2 row)
~~~
----
### 5.6 Aggregate Functions
The following aggregation functions are supported:
- LISTAGG
- MEDIAN
#### 5.6.1 LISTAGG
**Description**
Returns a concatenated, delimited list of string values.
**Syntax**

**General rules**
- LISTAGG concatenates and delimits a set of string values and returns the result.
- For *delimiter*, specify a string. If the delimiter is omitted, a list of strings without a delimiter is returned.
- The data type of the return value is TEXT.
**Example**
----
In the following example, the result with values of column col2 in table t1 delimited by ':' is returned.
~~~
SELECT LISTAGG(col2,':') FROM t1;
listagg
-------------------
AAAAA:BBBBB:CCCCC
(1 row)
~~~
----
#### 5.6.2 MEDIAN
**Description**
Calculates the median of a set of numbers.
**Syntax**
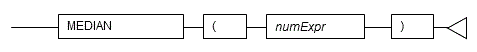
**General rules**
- MEDIAN returns the median of a set of numbers.
- The numbers must be numeric data type.
- The data type of the return value will be REAL if the numbers are REAL type, or DOUBLE PRECISION if any other type is specified.
**Example**
----
In the following example, the median of column col3 in table t1 is returned.
~~~
SELECT MEDIAN(col3) FROM t1;
median
--------
2000
(1 row)
~~~
----
### 5.7 Functions That Return Internal Information
The following functions that return internal information are supported:
- DUMP
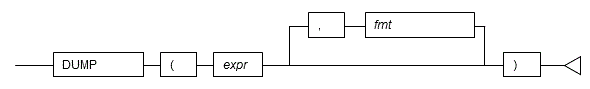
#### 5.7.1 DUMP
**Description**
Returns internal information of a value.
**Syntax**
**General rules**
- DUMP returns the internal information of the values specified in expressions in a display format that is in accordance with the output format.
- The internal code (Typ) of the data type, the data length (Len) and the internal expression of the data are output as internal information.
- Any data type can be specified for the expressions.
- The display format (base *n* ) of the internal expression of the data is specified for the output format. The base numbers that can be specified are 8, 10, and 16. If omitted, 10 is used as the default.
- The data type of the return value is VARCHAR.
**Note**
----
The information output by DUMP will be the complete internal information. Therefore, the values may change due to product updates, and so on.
----
**Example**
----
In the following example, the internal information of column col1 in table t1 is returned.
~~~
SELECT col1, DUMP(col1) FROM t1;
col1 | dump
------+------------------------------------
1001 | Typ=25 Len=8: 32,0,0,0,49,48,48,49
1002 | Typ=25 Len=8: 32,0,0,0,49,48,48,50
1003 | Typ=25 Len=8: 32,0,0,0,49,48,48,51
(3 row)
~~~
----
#### 5.8 Datetime Operator
The following datetime operators are supported for the DATE type of orafce.
**Datetime operator**
|Operation|Example|Result|
|:---:|:---|:---|
|+|DATE'2016/01/01' + 10|2016-01-11 00:00:00|
|-|DATE'2016/03/20' - 35|2016-02-14 00:00:00|
|-|DATE'2016/09/01' - DATE'2015/12/31'|245|
**Note**
----
If using datetime operators for the DATE type of orafce, it is necessary to specify "oracle" for search_path in advance.
----
**See**
----
Refer to "Notes on Using orafce" for information on how to edit search_path.
----